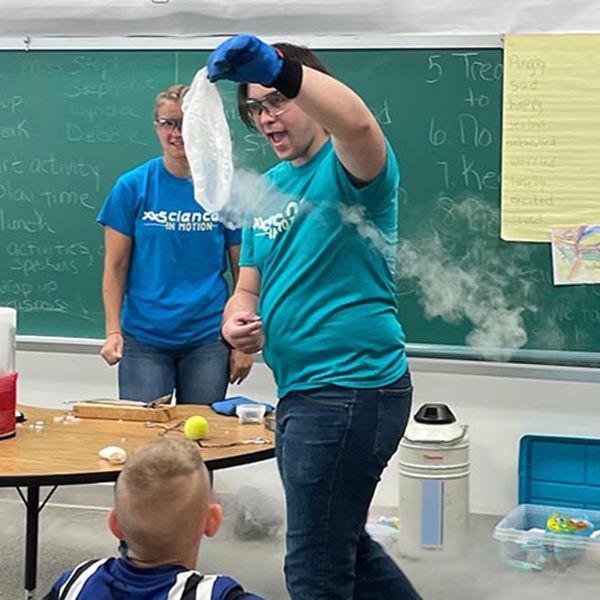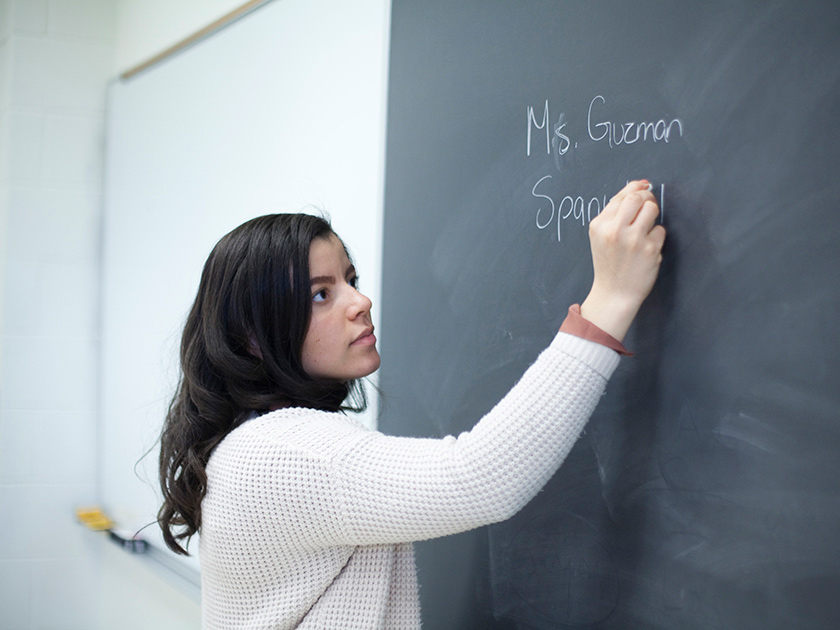
The Education Department at Juniata is accredited by the Pennsylvania Department of
Education to offer certification programs in PreK-4th grade early childhood education,
special education, secondary education, and world language education.
For all areas of certification, carefully planned field experiences provide opportunities
to develop teaching skills and apply concepts under the supervision of Juniata faculty
and well-qualified cooperating teachers. These field placements begin in your first
year and continue through graduation, giving you the opportunity to get multiple real-world
experiences that will complement and enhance your on-campus courses. The culmination
of our teacher preparation program is student teaching in local schools.
Create your Program of Emphasis highlighting education studies and another field of interest like child-life studies, environmental studies, or human development.
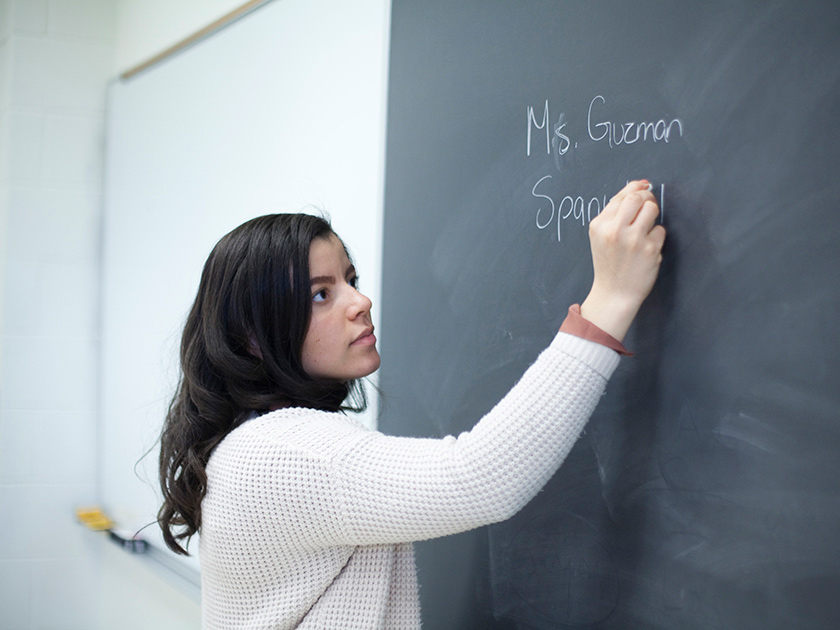
The Education Department at Juniata is accredited by the Pennsylvania Department of
Education to offer certification programs in PreK-4th grade early childhood education,
special education, secondary education, and world language education.
For all areas of certification, carefully planned field experiences provide opportunities
to develop teaching skills and apply concepts under the supervision of Juniata faculty
and well-qualified cooperating teachers. These field placements begin in your first
year and continue through graduation, giving you the opportunity to get multiple real-world
experiences that will complement and enhance your on-campus courses. The culmination
of our teacher preparation program is student teaching in local schools.
Create your Program of Emphasis highlighting education studies and another field of interest like child-life studies, environmental studies, or human development.
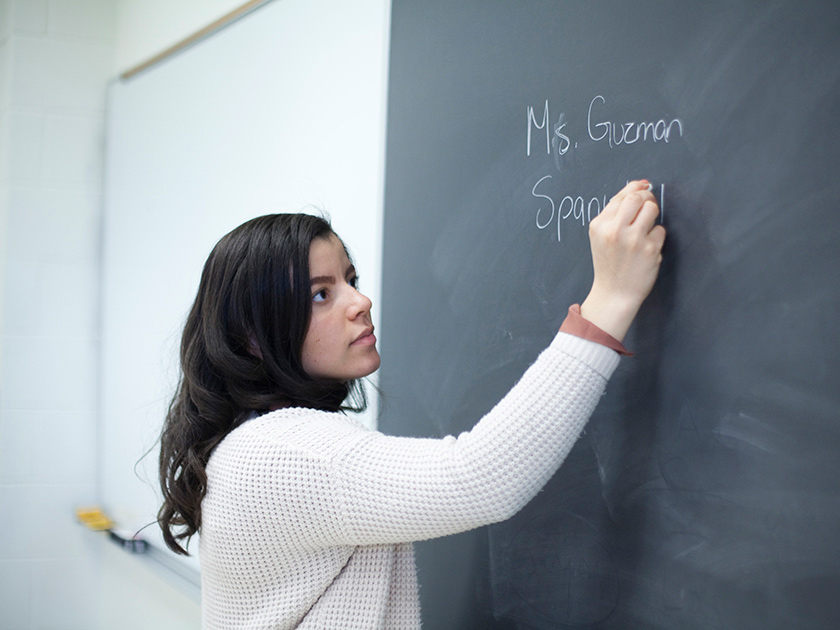
The Education Department at Juniata is accredited by the Pennsylvania Department of
Education to offer certification programs in PreK-4th grade early childhood education,
special education, secondary education, and world language education.
For all areas of certification, carefully planned field experiences provide opportunities
to develop teaching skills and apply concepts under the supervision of Juniata faculty
and well-qualified cooperating teachers. These field placements begin in your first
year and continue through graduation, giving you the opportunity to get multiple real-world
experiences that will complement and enhance your on-campus courses. The culmination
of our teacher preparation program is student teaching in local schools.
Create your Program of Emphasis highlighting education studies and another field of interest like child-life studies, environmental studies, or human development.
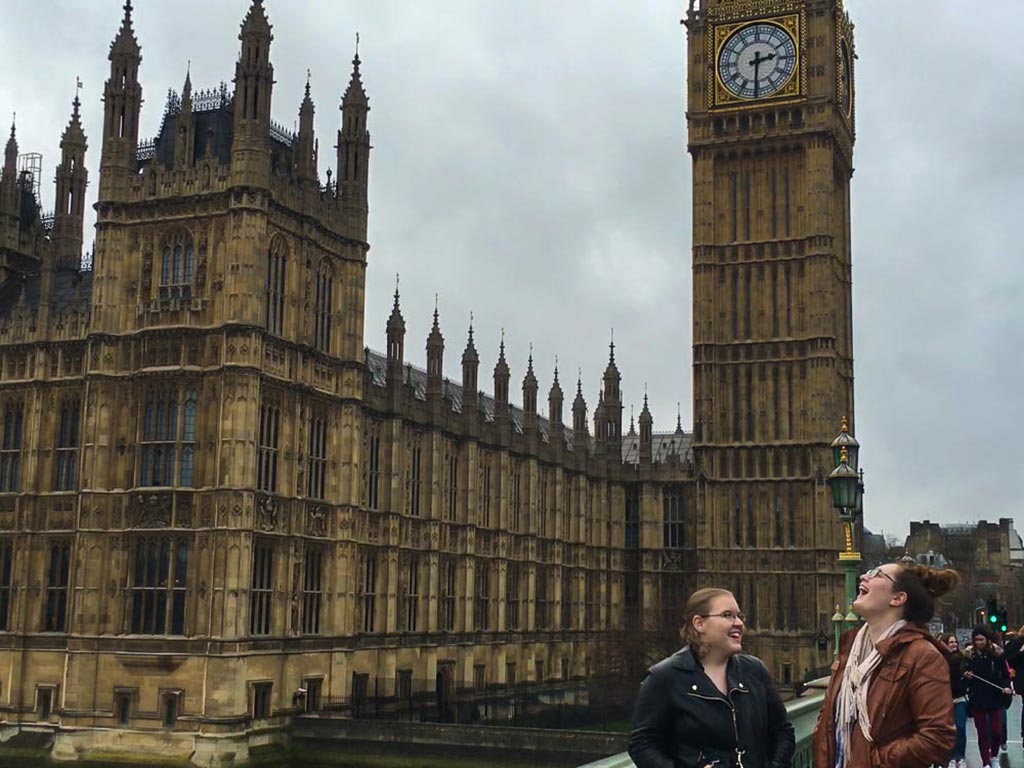
Study Abroad
Education students are encouraged to study abroad for a semester or participate in one of the many short term study abroad programs that are offered. It is possible for teacher candidates to consider study abroad sites in England, Australia, China, Ecuador, France, Germany, Greece, Scotland, India, Ireland, New Zealand, Northern Ireland, Japan, Mexico, and Spain. Learn more about study abroad programs in education here.
Education Certifications
- Biology and Secondary Education
- Chemistry and Secondary Education
- Early Childhood Education (PreK-4th Grade)
- Early Childhood Education (PreK-4th Grade) & Special Education (PreK-12th Grade)
- Earth & Space Science Secondary Education
- English Secondary Education
- General Science and Secondary Education
- Mathematics and Secondary Education
- Physics and Secondary Education
- Social Studies Secondary Education
- Spanish Education
 skip to content
skip to content










